What is Nanotechnology ?
Nanotechnology is a branch of science and technology that involves the use of techniques that allow the manipulation of matter on an atomic and molecular level. 1 nanometer = 0.000000001 meters. When working on materials at the nanoscopic scale novel and unique properties emerge due to the high surface area to volume ratio. These properties differ significantly from the same material at the bulk or macro scale. Nanotechnology seeks to use these unique properties to its advantage for various industrial and research applications to create better products and technologies for the betterment of the world.
Applications
This nano materials is one with a broad range of applications across multiple domains, acting as a raw material for products as disparate as cigarette filters and cosmetics.

Cosmetics
Zinc oxide is used in a wide range of cosmetics and personal care products including makeup, nail products, baby lotions, bath soaps and foot powders. Zinc oxide is also used in skin protectants, such as diaper rash ointments and sunscreen products.
Uses & Benefits
Zinc oxide is used as a bulking agent and a colorant. In over-the-counter drug products, it is used as a skin protectant and a sunscreen. Zinc oxide works as a sunscreen by reflecting and scattering UV radiation. Sunscreens reduce or prevent sunburn and premature aging of the skin.
Skin Treatment
Calamine lotion is made using zinc oxide powders, as are any number of other ointments, creams, washes, rinses, and other treatments used to control or prevent certain skin diseases.
Agriculture Industry Use of Zinc Oxide:
It’s important to note that while zinc oxide nano powder offers promising benefits, its use in agriculture should be approached with caution. The potential environmental and health implications of nanoparticles need to be thoroughly studied and understood. Regulations and guidelines should be followed to ensure the safe and responsible use of nanomaterials in agriculture. Additionally, the specific application and dosage of zinc oxide nano powder will depend on the type of crop, soil conditions, and local regulations, so it’s advisable to consult with agricultural experts or extension services before using such products in farming practices.


Role in Food
Zinc oxide is fairy common as a food additive in fortified processed meals such as breakfast cereal. This is done to supplement zinc, which can't be digested in it's pure form.
Zinc oxide in food is fortification
Zinc oxide may be found in breakfast cereals, nutrition drinks and nutrition bars. The amount of zinc oxide added to food may vary. Reading the food label and ingredients list can help you identify foods fortified with the mineral.
Zinc is used in crystalline glazes
zinc is used in crystalline glazes (typically 25%), because these have no clay content, they bring out the best and worst of both the calcined and raw materials.
Ceramic grades are often calcined to remove any physical water (so they do not clump in the bag). But these grades also have a larger particle size and lower surface area (e.g. 3 square meters per gram vs. less than 1; however 99.9% still passes 325 mesh). While calcined grades are said to produce less glaze surface defect problems, many ceramists have used the raw grades without serious issues. You can calcine (or re-calcine) zinc on your own in a bisque kiln at around 815C. However there are issues: First, because the calcined zinc wants to rehydrate (and get lumpy in the process) you must store it in an airtight container (some people calcine a mix of zinc and kaolin to prevent this, but theoretically such a mix should not even need to be calcined). Second, the calcined zinc may produce slurry thickening issues over time. Many zinc-bearing frits are available (e.g. Fusion FZ-16 has 15% ZnO) and incorporating one of them to source it instead of raw zinc oxide will produce glazes that are more fusible, have better clarity and fewer defects (a classic job for glaze chemistry calculations).

Our Amazing Feature
A fine powder ranging in color from white to light yellow, this material is composed of 99.8% or purer zinc oxide particles ranging from 10nm to 3nm in diameter.
What is Titanium Oxide
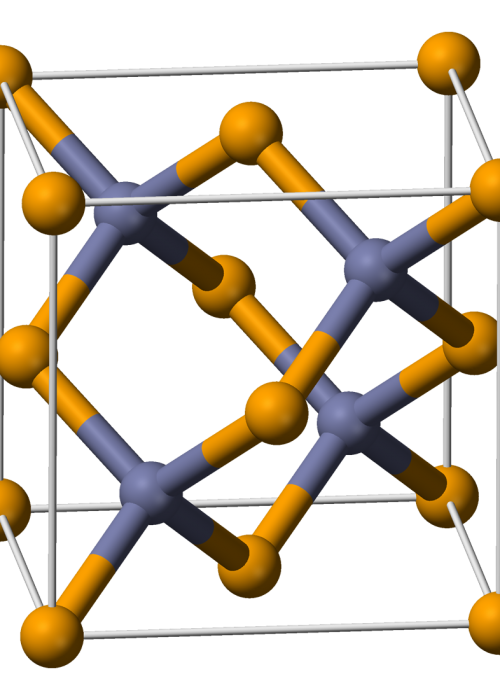
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania, is the naturally occurring oxide of titanium, chemical formula TiO ₂. When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6, or CI 77891. Generally, it is sourced from ilmenite, rutile and anatase.Titanium dioxide occurs in nature as the well-known minerals rutile, anatase and brookite, and additionally as two high pressure forms, a monoclinic baddeleyite-like form and an orthorhombic α-PbO2-like form, both found recently at the Ries crater in Bavaria.
What is Zinc Oxide
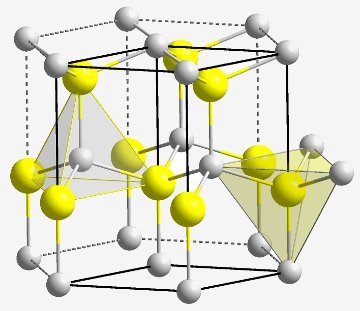
Zinc oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula ZnO. ZnO is a white powder that is insoluble in water, and it is widely used as an additive in numerous materials and products including rubbers, plastics, ceramics, glass, cement, lubricants, paints, ointments, adhesives, sealants, pigments, foods, batteries, ferrites, fire retardants, and first-aid tapes. Although it occurs naturally as the mineral zincite, most zinc oxide is produced synthetically.
What is New in Nanotechnology ?
Sorry, no posts matched your criteria.
-
Continue Working
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in.
-
Visions Helps You
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in.
-
Eastside Massage
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris nisi ut aliquip ex ea commodo consequat. Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in.
